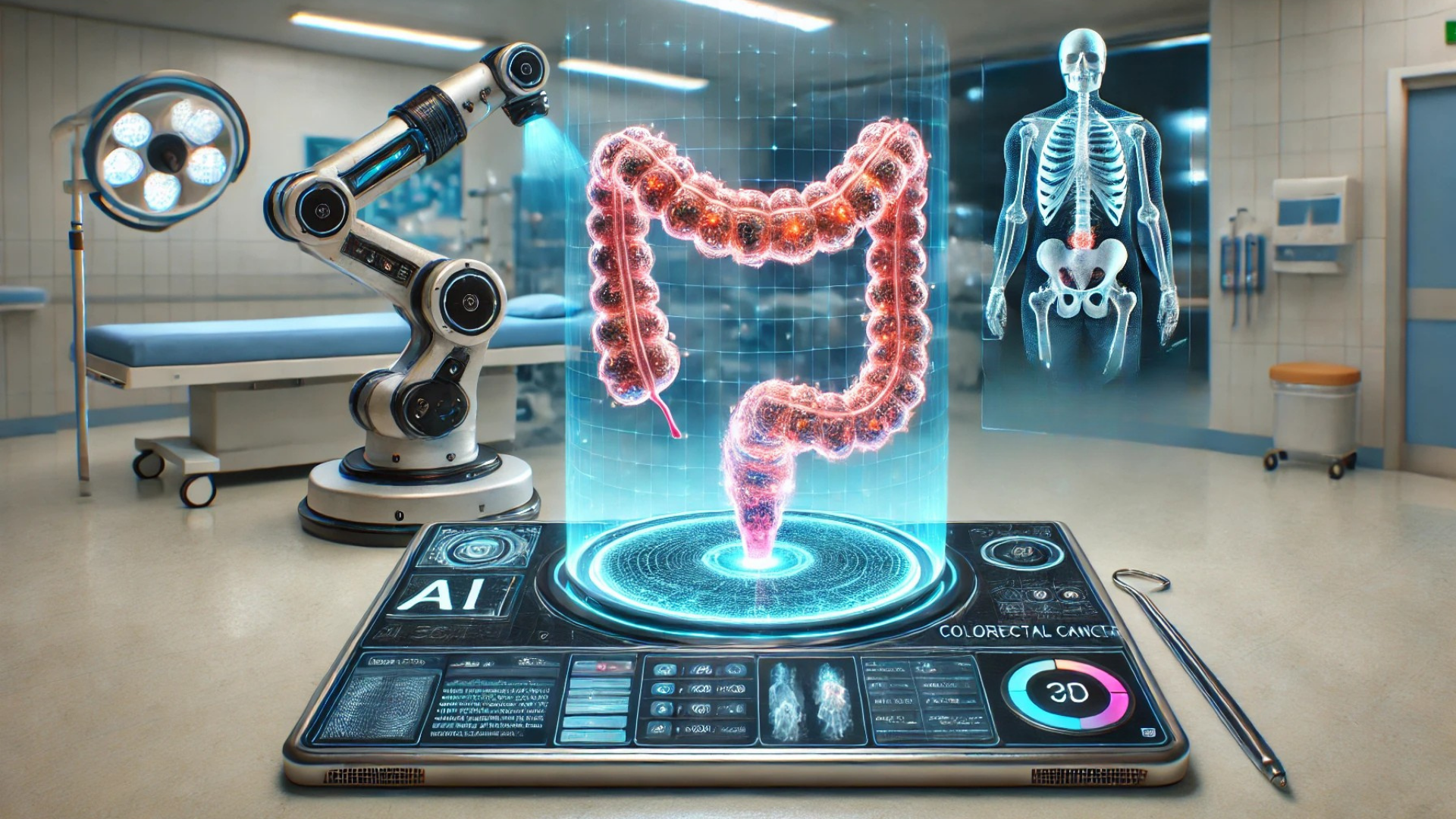
A groundbreaking AI-based tool for detecting colorectal cancer through tissue sample analysis has been developed at the University of Jyväskylä. The artificial neural network model has achieved unprecedented accuracy in classifying tissue samples, surpassing all previous models. In a major step toward advancing cancer diagnostics, the research team has made the tool freely available to encourage further research and development.
Revolutionizing Cancer Detection with AI
Developed in collaboration with the University of Turku’s Institute of Biomedicine, University of Helsinki, and Nova Hospital of Central Finland, the AI-powered tool automates colorectal cancer tissue analysis with remarkable precision. The neural network model demonstrated an accuracy rate of 96.74%, making it the most effective AI tool to date for cancer tissue classification.
“Based on our study, the developed model is able to identify all tissue categories relevant for cancer identification, with an accuracy of 96.74%.”
– Fabi Prezja, Doctoral Student, University of Jyväskylä
How the AI Tool Works
Traditionally, pathologists manually analyze digital microscopy slides, marking cancerous and related tissues point by point. The new AI tool automates this process, scanning and highlighting different tissue categories in samples. This advancement could significantly reduce the workload for histopathologists, allowing for faster diagnoses, prognoses, and clinical insights.
Free Availability to Advance Research
To encourage collaboration and further breakthroughs, the research team has made the AI tool freely available. This initiative aims to accelerate cancer research and AI development by allowing scientists, developers, and medical professionals worldwide to refine and expand the tool’s capabilities.
“The free availability aims to accelerate future advances by encouraging scientists, developers, and researchers worldwide to continue developing the tool and finding new applications for it.”
– Fabi Prezja
Caution Before Clinical Implementation
Despite the promising results, researchers stress that AI tools must be introduced into clinical settings gradually and with caution. Before being adopted for routine use, rigorous validation processes are required to ensure the tool meets clinical and regulatory standards.
With its exceptional accuracy and potential to streamline cancer diagnostics, this AI-powered tool marks a significant step forward in medical AI applications. As research and validation continue, it could become a vital asset in the fight against colorectal cancer.